
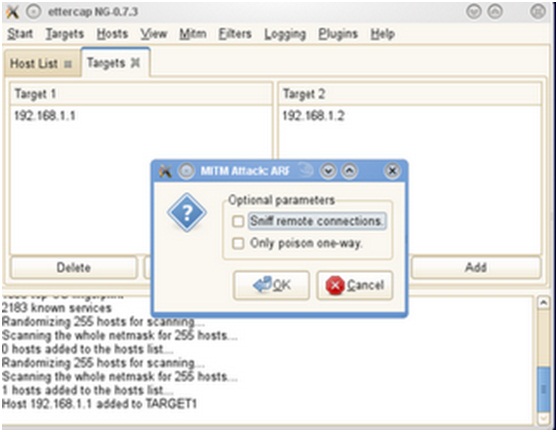
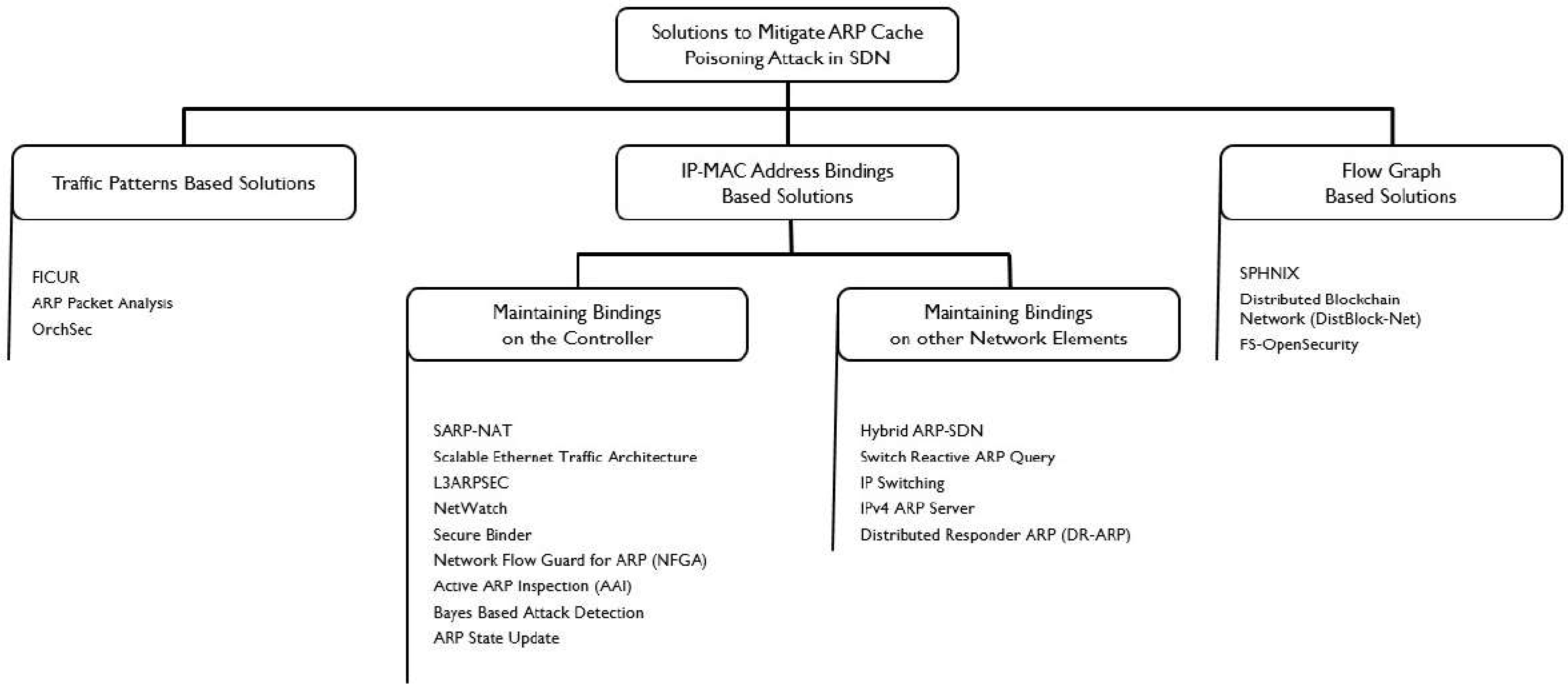
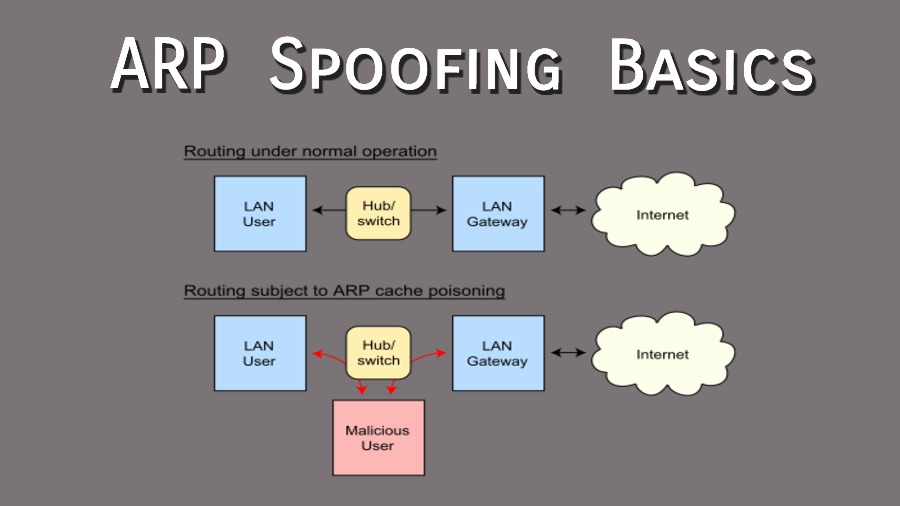
What is ARP Spoofing (ARP Poisoning)Īn ARP spoofing, also known as ARP poisoning, is a Man in the Middle (MitM) attack that allows attackers to intercept communication between network devices. However, since most of the Internet still uses the older IPv4 protocol, ARP remains in wide use. The newer IPv6 protocol uses a different protocol, Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP), which is secure and uses cryptographic keys to verify host identities.

See our terms & privacy.ĪRP only works with 32-bit IP addresses in the older IPv4 standard. This is a weak point in the ARP protocol, which opens the door to ARP spoofing attacks. It also lets hosts accept ARP responses even if they never sent out a request. The ARP protocol was not designed for security, so it does not verify that a response to an ARP request really comes from an authorized party. If the host doesn’t know the MAC address for a certain IP address, it sends out an ARP request packet, asking other machines on the network for the matching MAC address. Hosts maintain an ARP cache, a mapping table between IP addresses and MAC addresses, and use it to connect to destinations on the network. Most commonly, devices use ARP to contact the router or gateway that enables them to connect to the Internet. ARP translates Internet Protocol (IP) addresses to a Media Access Control (MAC) address, and vice versa. 3 How to Detect an ARP Cache Poisoning AttackĪddress Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol that enables network communications to reach a specific device on the network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
